This ensures greater privacy to the users but also protect against eavesdropping of the NSA and others. Thanks to the TOR network nobody can know:
- Who are you.
- With whom you are communicating.
- If you are communicating.
- What are you reading or writing.
- Where are you.
- Where is the server.
- Whar you are doing.
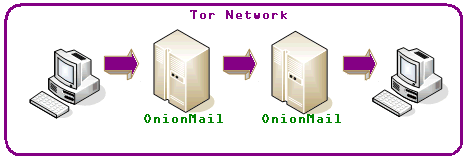
To use OnionMail all you need is an email client connected to the TOR network without install any special or complicated software. (Example: Claws-Mail or Thunderbird).
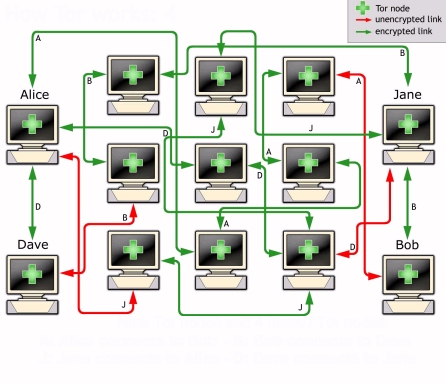
All OnionMail server are connected in a federated network to check the SSL certificates and working state. All federated server can connect to the Internet via exit/enter servers to forward messages between networks.
OnionMail through the exit/enter nodes forwards messages between networks TOR and internet in a transparent manner.
TOR =? TOR
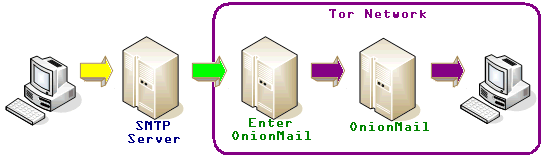
Internet =? TOR
TOR =? Internet
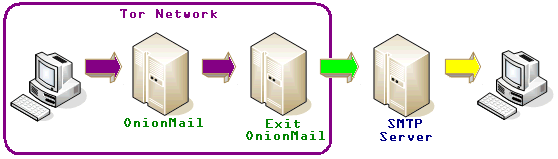
Some special protocols implement the possibility not to use obligatory the TOR network addresses with 16 alphanumeric characters using the address registered with the enter/exit servers.
Nobody is obligated always to use the addresses of 16 characters of the TOR network.
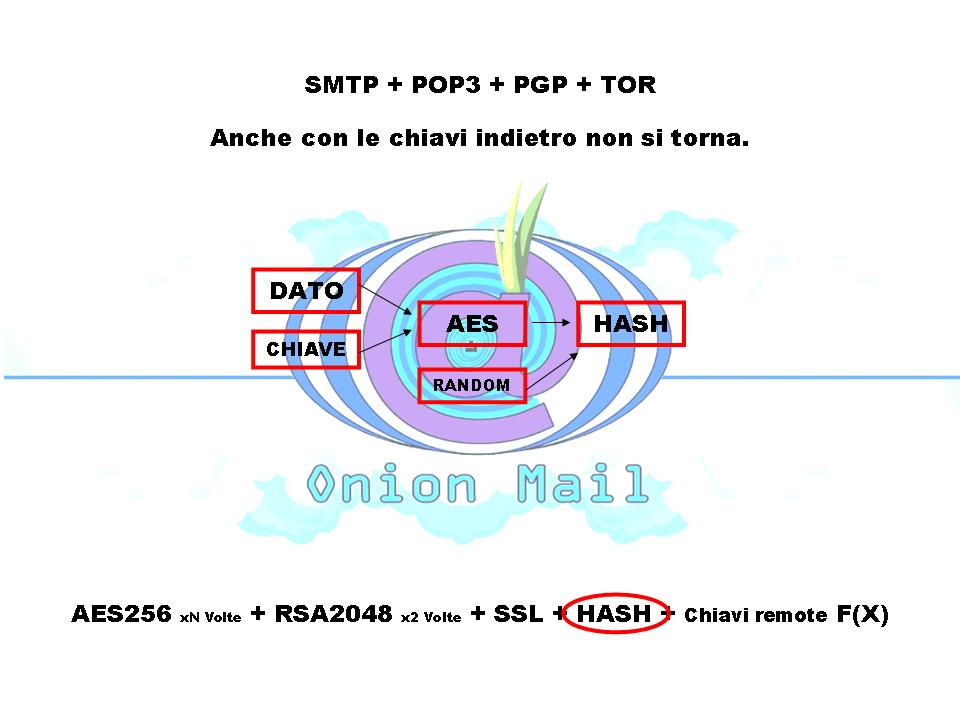
In the event of theft OnionMail does not reveal any sensitive data:
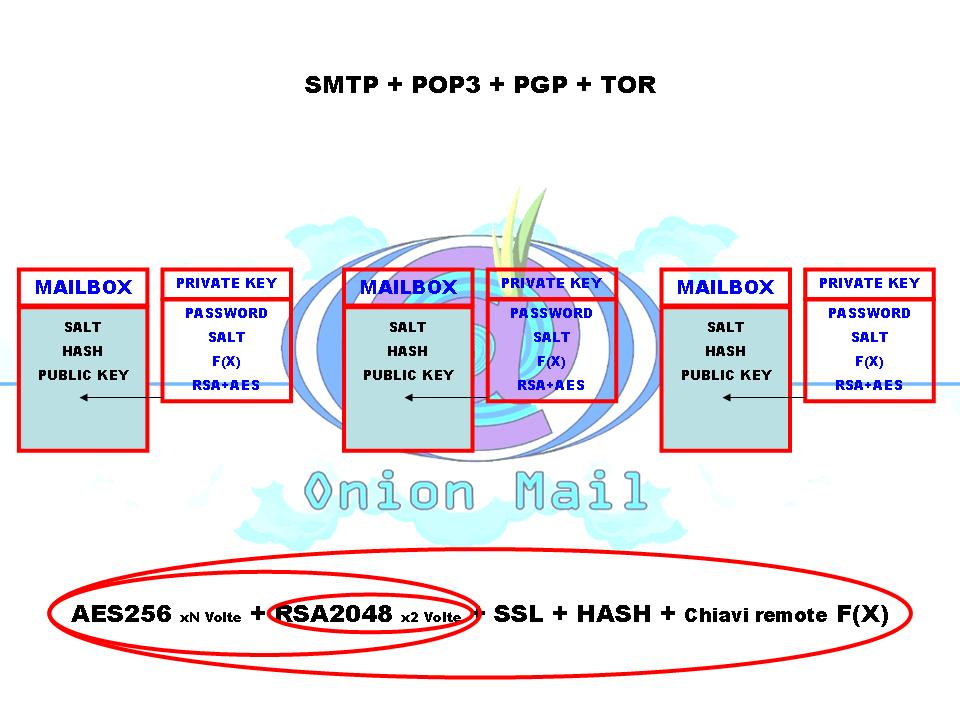
The OnionMail server type uses asymmetric encryption. Each inbox are encrypted with RSA asymmetric keys encrypted with different users' passwords. Obtaining the keys of the server nobody can read messages from users' inbox.
All data are saved in encrypted form and chopped files using an hash algorithm. In this way an attacker can't obtain the reverse path to get informations or metadata of any users and their activities.
Every file is deleted via wipe to prevent forensic recovery of messages or other user's data.
All files, users and inbox are encrypted via rolling key calculated form hash algorithm and some server's keys. The master key of the server is not on the server:
When an OnionMail server start it negotiate some function F(X) with other servers. The keys are chopped, encrypted and calculated from a lot of F(X) spread into the TOR network.
All F(X) are controlled by auto destruction KCTL certificates.
The auto destruction certificate can activate, deactivate or destroy the keys on all F(X) nodes without access the original OnionMail server.
This provides the ability to delete the keys of the server in the event of theft or seizure without require server access.
Spam is short-lived because there are the custom blacklists. So each user can set their own spam filters.
OnionMail contains a little bot to communicate with the server directly. This bot is used to activate the OnionMail's extended functions. It supports PGP encrypted messages, mailing lists, spam filters and much more...
In the OnionMail's network are introduced some types of e-mail addresses. Some suffix of mail address are reserved to get the type of mail address: User, M.A.T. Protocol address, SysOp, servers, mailing list and applications.
All OnionMail server are anonymous and the system administrator can't read any message or get a list of users. With other configurations the system administrator can give an invite code to user to subscribe only one mail address. This way is used to change the subscription policy.
To create a new OnionMail's mailbox can be used three ways:
- Using the registration via web (at the TOR hidden service).
- Using the wizard for TAILS.
- Sending a message NEWUSER to the server with your public PGP key to get your account settings.
- Multiple instances of server. (multiple indipendent hidden services).
- Native PGP integration for subscriprion and server`s message.
- Subscription via PGP encrypted email.
- VMAT Protocol (can use normal mail address without .onion).
- SSL cryptography by default. (STARTTLS 2048 bits)
- Multiple encryption everywhere, RSA + AES + RSA + AES with salt.
- Support unicode password (UTF-8 password and 2048 bits keyfiles).
- Inhibition of store any message in relay server.
(Only direct connection is allowed without multiple connections). - Metadata protection. NSA or GCHQ can't read your metadata.
- SMTP Compatibility.
- Internet normal email compatibility.
- AntiSpam, blacklist and realtime filters.
- Decentralized trust system for SSL certificate and public keys and exit list.
- Native mailing list support.
- Garbage collector to remove automatically old messages.
- Clock and time zone spoofing.
- Server services and operations:
Add / Remove mail address or mail server in blacklist.
Mailing list Subscribe / Unsubscribe.
Request of server "rulez". (Server help).
(All via mail message to the server directly "server@ xyz... .onion ") - JAVA Implementation for all platform.
- Localhost control port and server API.
- Protected server password and keys not saved on the server.
- IP BlackList
- Onion BlackList
- RSA Server and Tor connection authentication.
- Connections via Tor Network.
- Enter/Exit server to connect Tor to Internet and viceversa.
- Statistics in csv format.
- Strong cryptography (RSA 2048 bits, AES 256 + AES 256 + AES 256 x 7).
- Password key derivation via multiple keyfiles and passwords.
- Deleting files with wipe by default.
- Message headers filtering to hide informations and sigint.
- POP3 TLS Access.
- SMTP TLS Access.
- User's parameters.
- Exit node selection to connect to internet.
- M.A.T. Protocol to connect correctly Internet, Tor, email and OnionMail.
- Server identification request via email to obtain the ssl certificate fingerprint.
- Self headers rebound to verifiy the client's mail headers and OnionMail filtering.
- AntiSpam system.
- Web HTTP interface.
- PGP version spoofing.
- Unlimited aliases.
- OnionMail server directory.
- Server configuration wizard.
- User subscription wizard (on TAILS).
- Mail applications interface.
- Mailing list support.
- Hidden mailing list support.
- Text CAPTCHA subscritpion.
- Server's PGP Keys.
- Editable rulez files.
- Web dynamic pages via OnionMail's ETEX system.
- Web SVG counter.
- M.A.T. Protocol.
- V.M.A.T. Protocol.
- Autodestruction certificates KCTL.
- Mail queue (only exit server).
- Multi delivery (TOR and Internet addresses).
- TKIM server authentication.
- Mail address authentication.
- Sender verify via SMTP test.
- Remote passphrase server.
- Remote start/stop and controlPort.
- Remote DNS_MX query via exit/enter node.
- F(X) remote keys function (BOOT/PUSH/DERK).
- And much more.....





